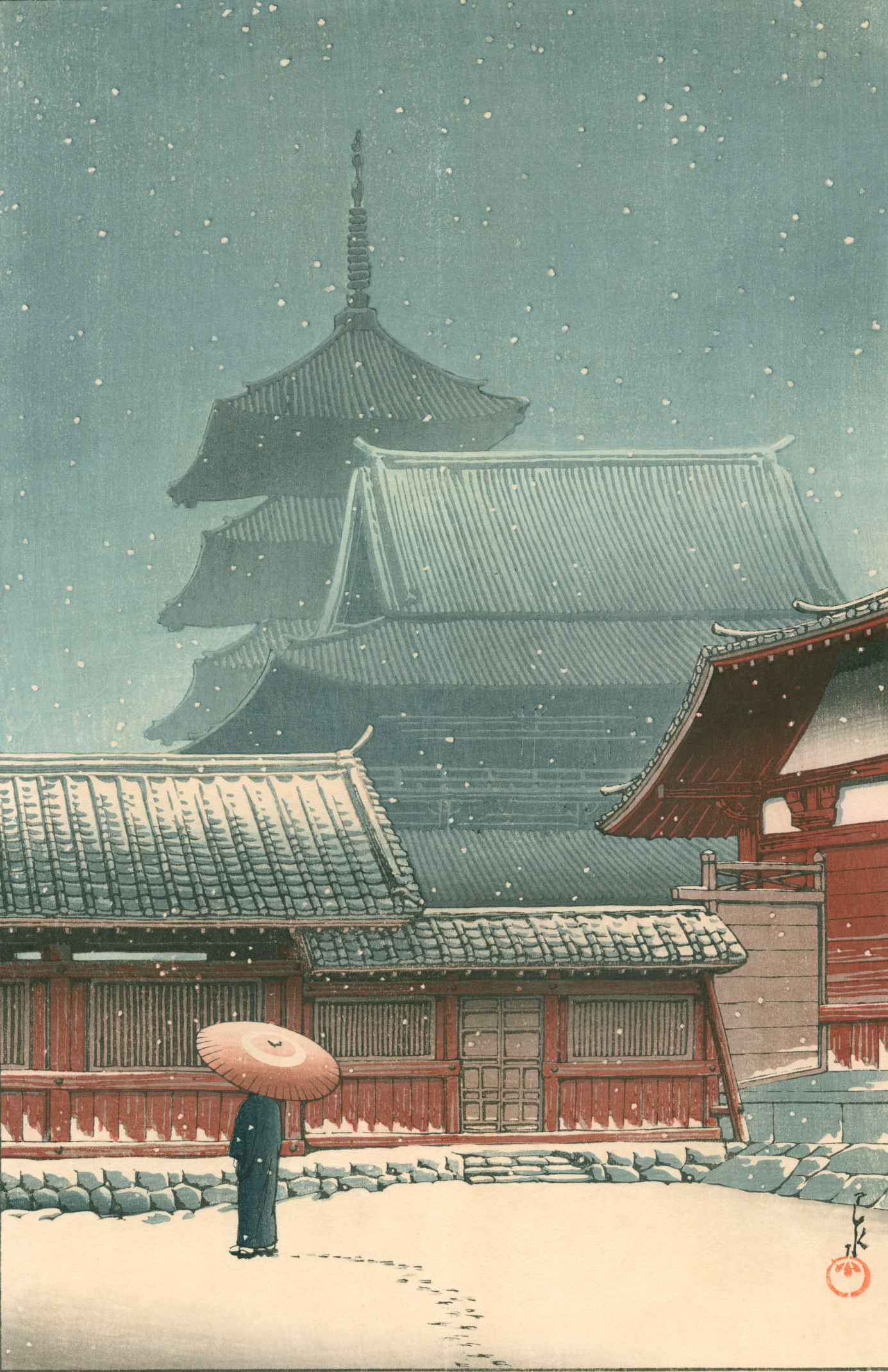
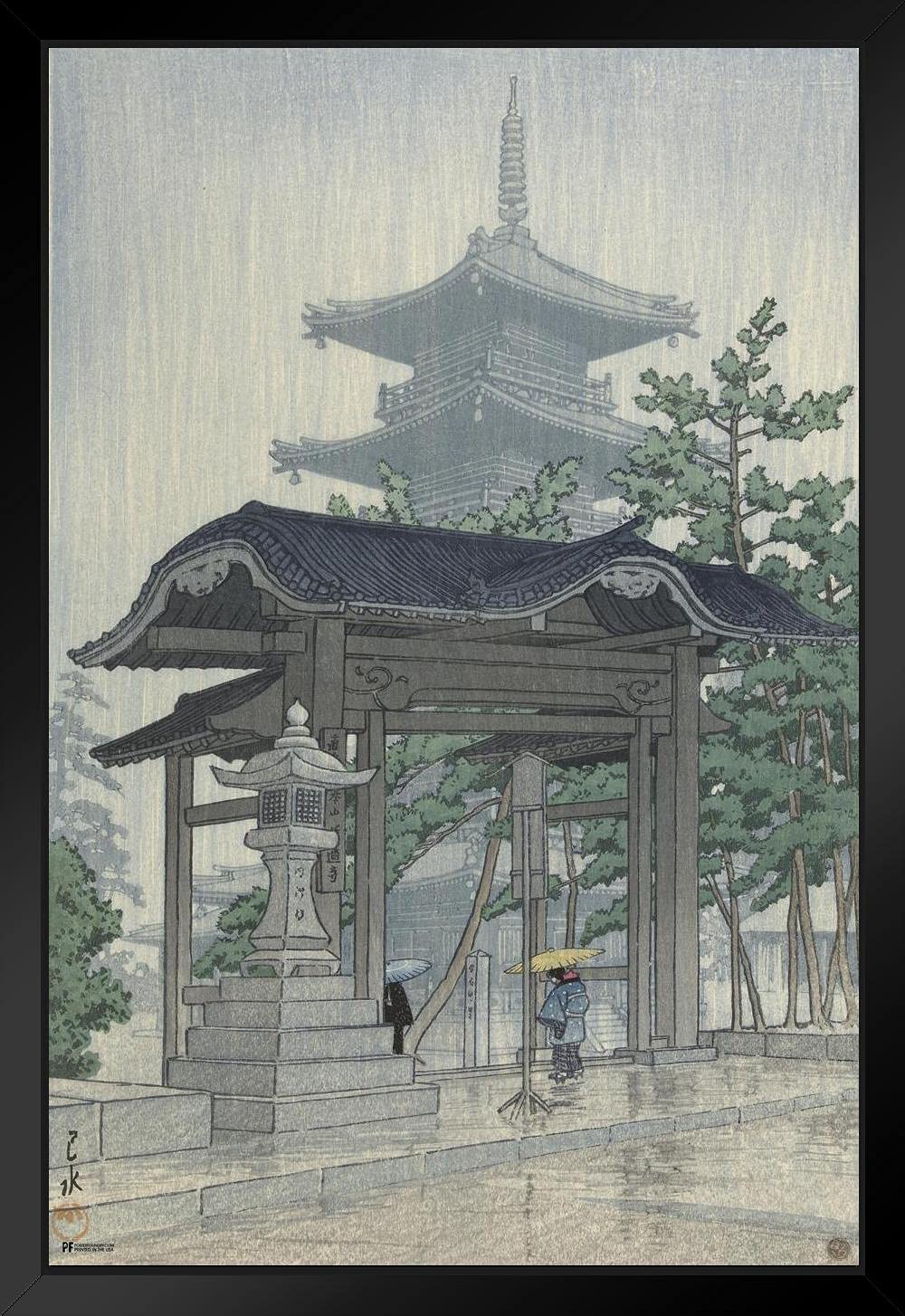
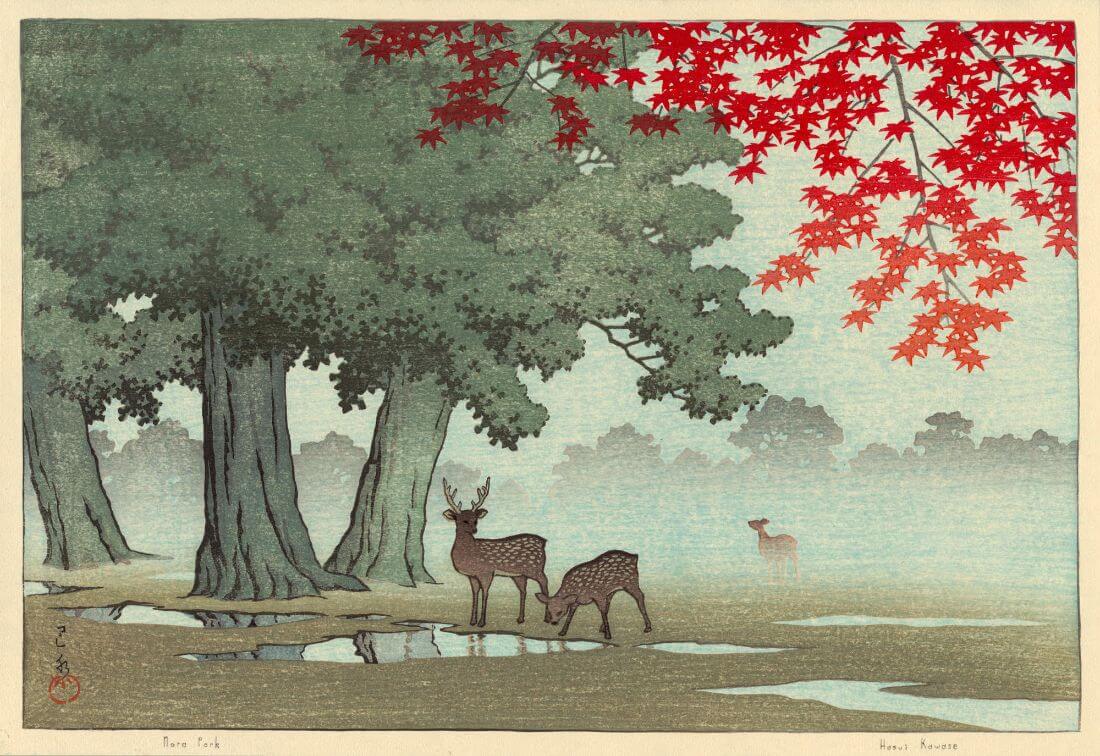
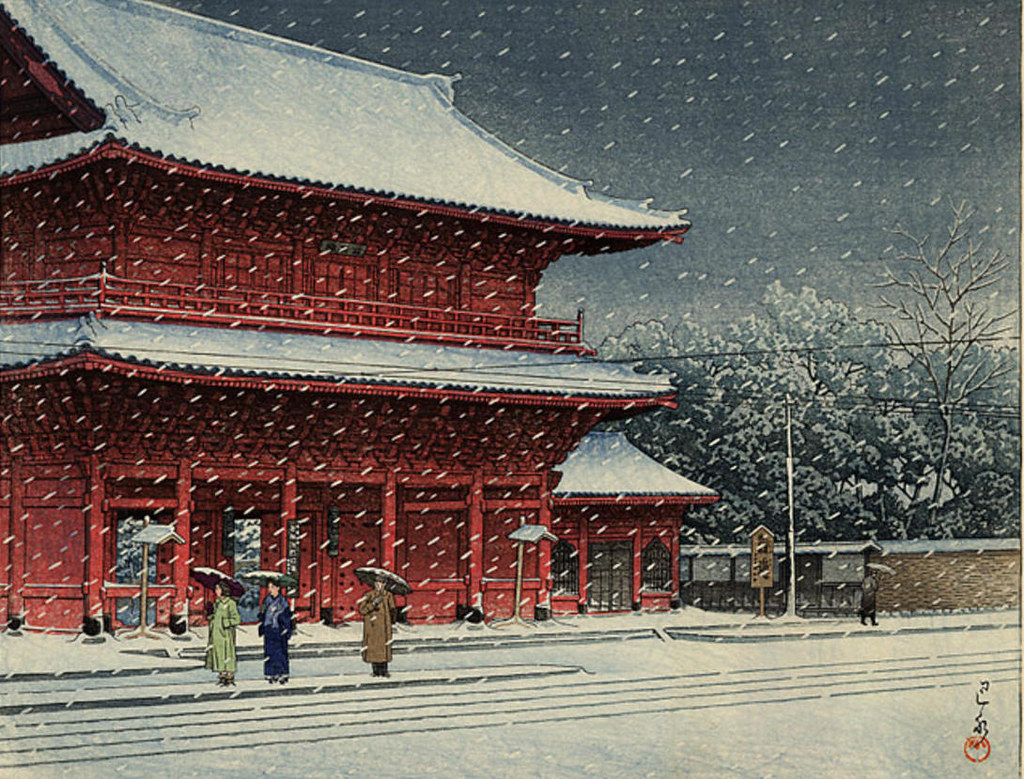
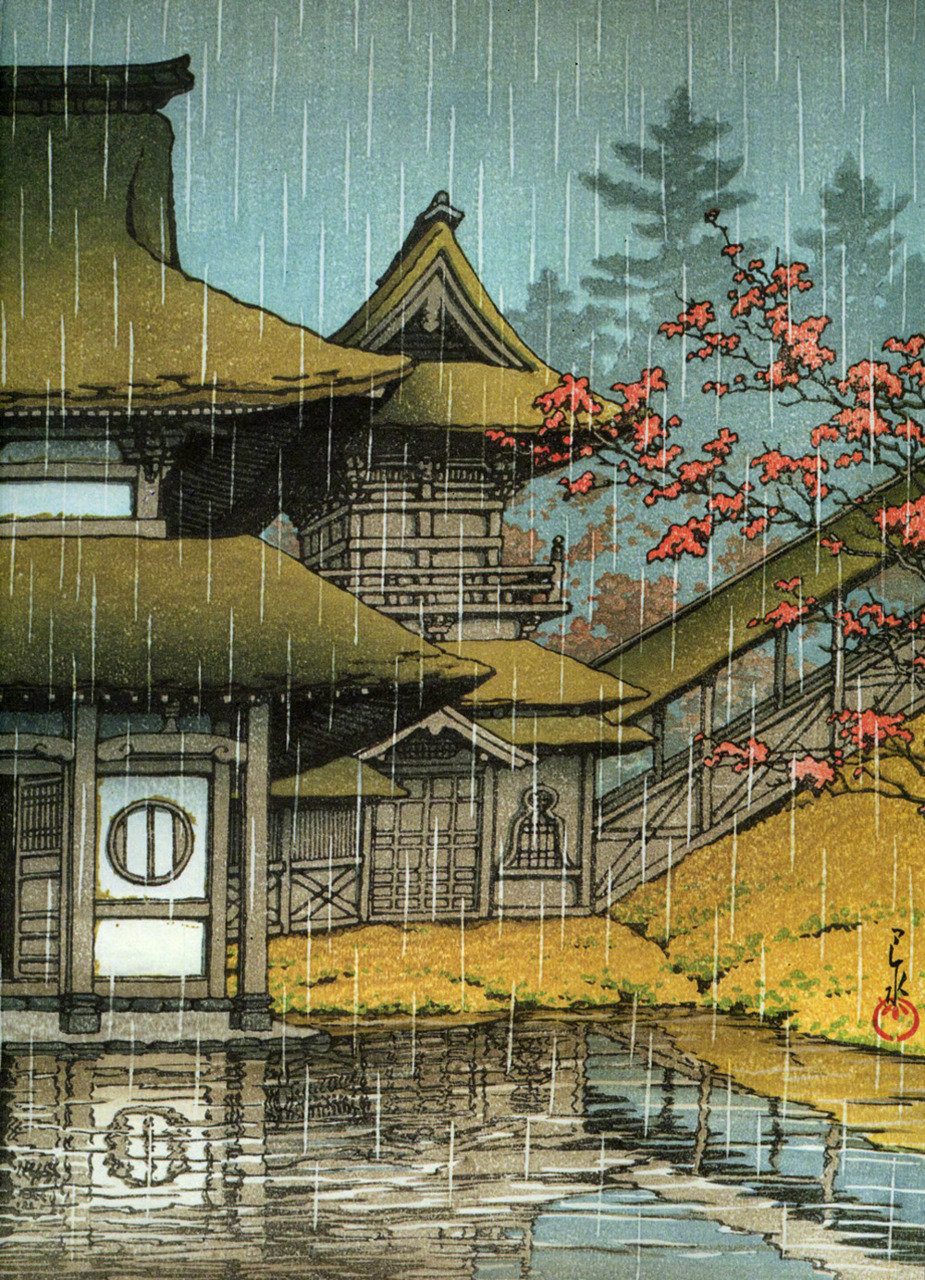
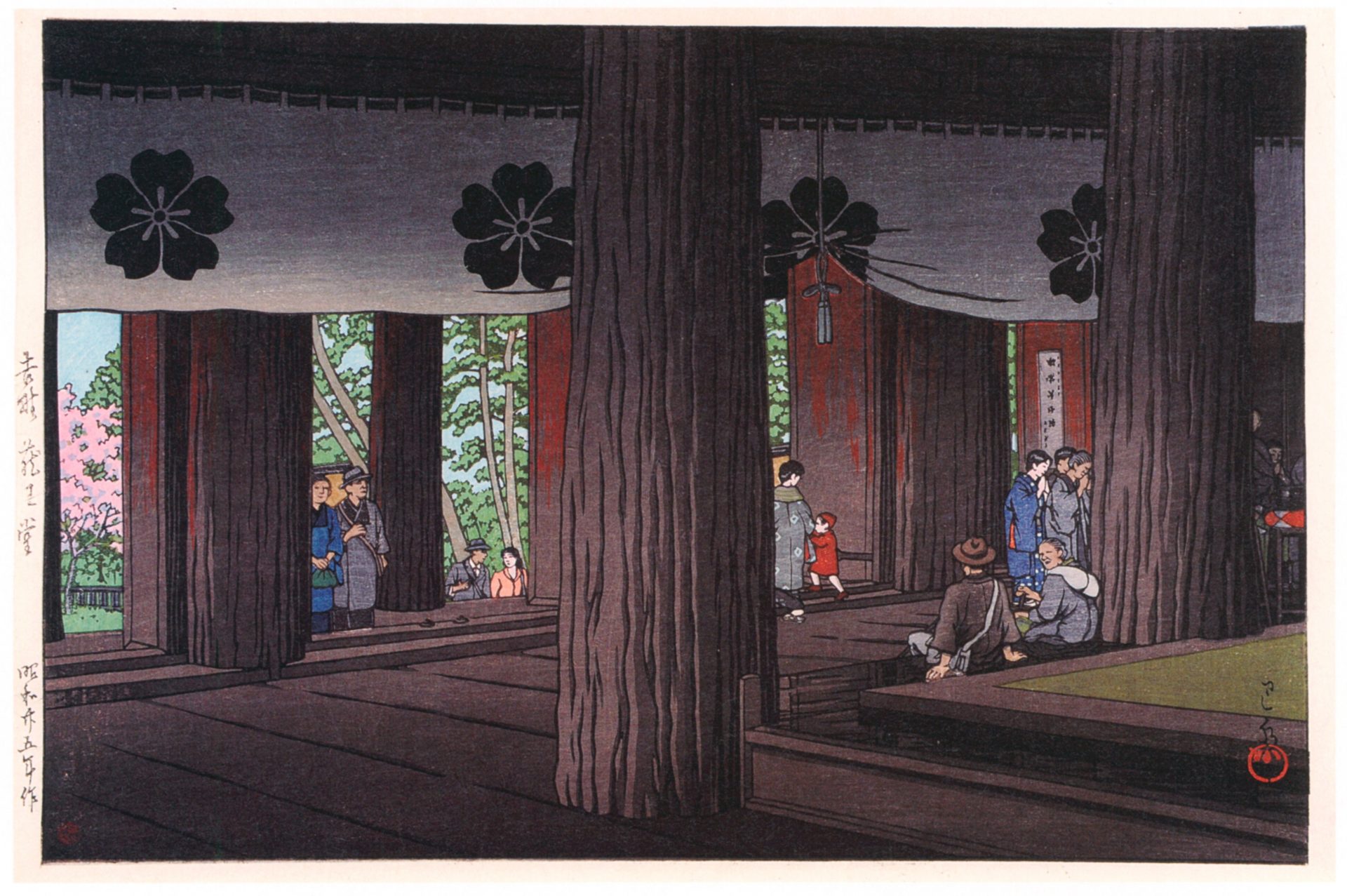
Hasui Kawase – The Art of Japan. Fine Japanese Prints. Title: Tennoji – Osaka. Date: 1927. Materials: woodblock print. Dimensions: 15.2 x 20.2 cm. Publisher: Watanabe. Source: https://www.theartofjapan.com/art-detail/?inv=10196353&at=Hasui. I have changed the light and contrast of the original photoAr
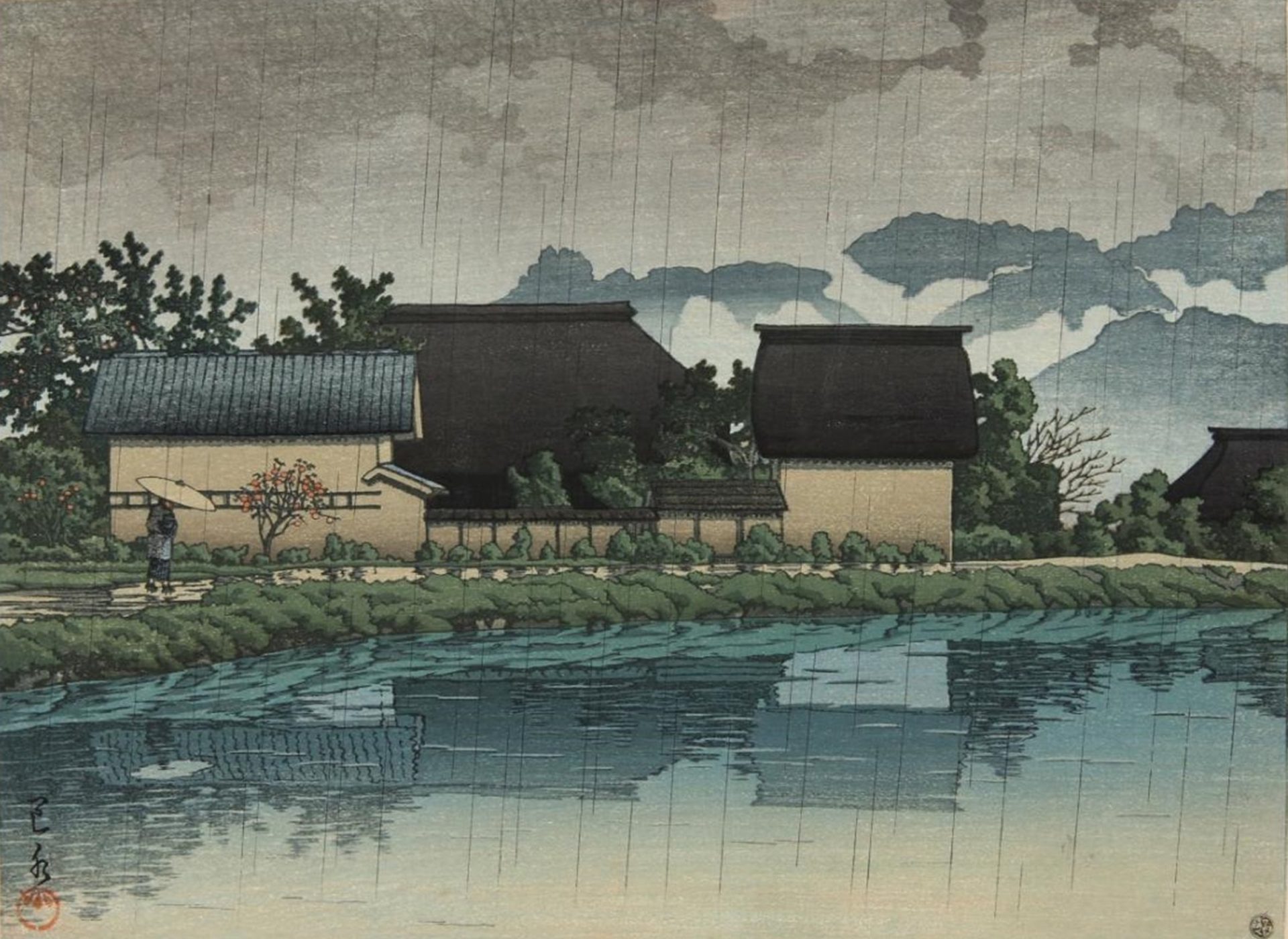

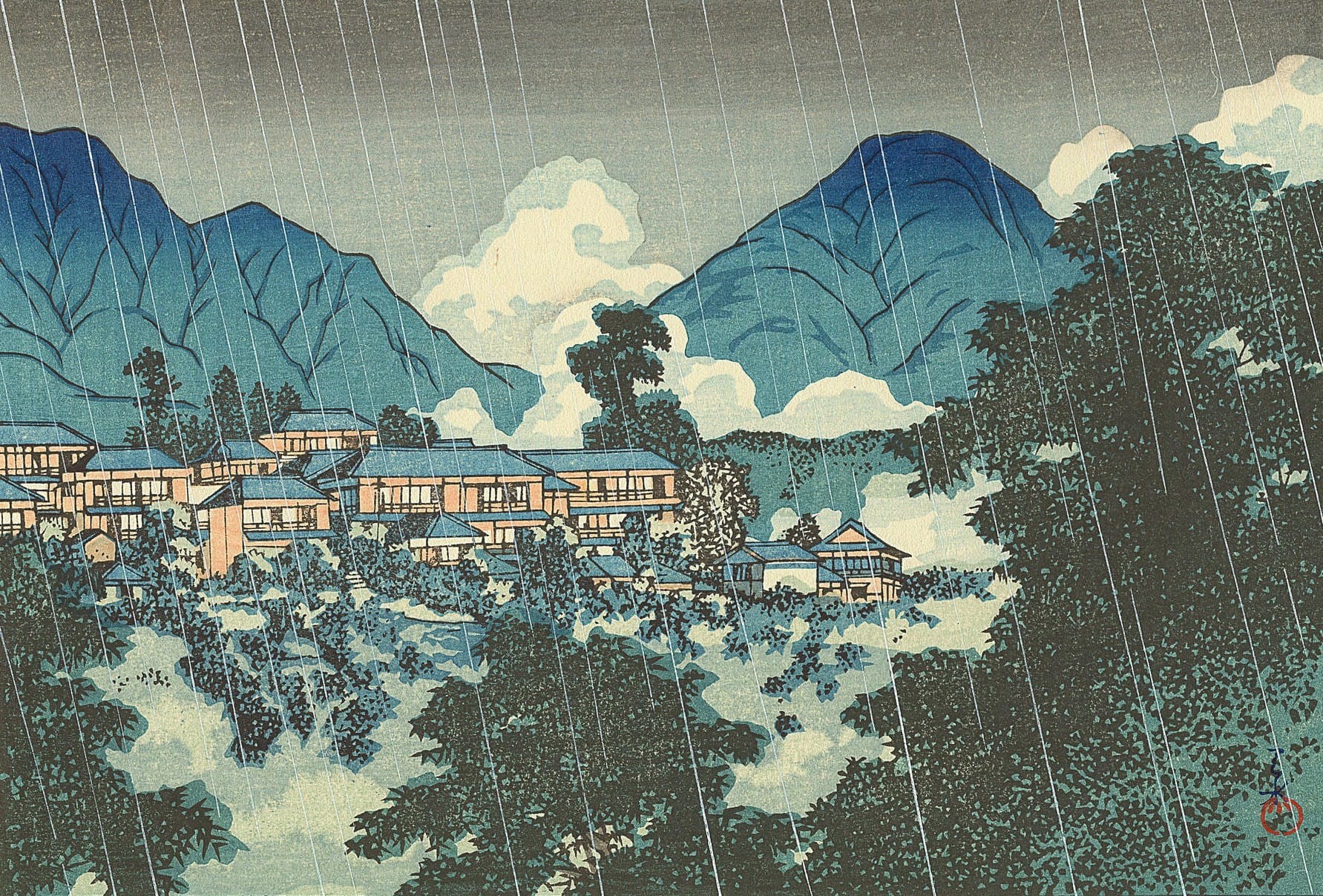
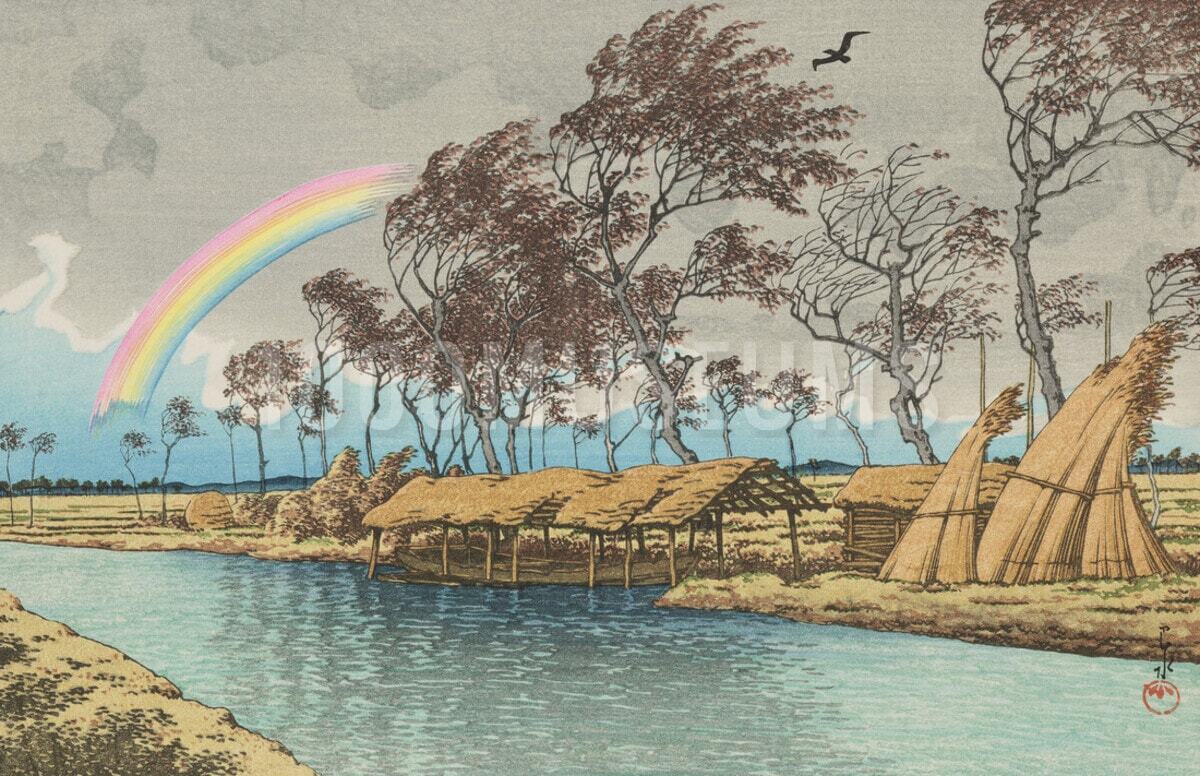
Hasui Kawase – private collection. Title: Farm Houses along a Canal in the Rain. Date: 1946. Materials: woodblock print. Dimensions: 38 x 25 cm. Auctioned by Lempertz in Cologne, on June 14, 2014. Source: https://www.lempertz.com/typo3temp/_processed_/csm_Lempertz-1034-1053-Asiatische-Kunst-Kawase-Hasui-1883-1957-_2e2599502d.jpg.
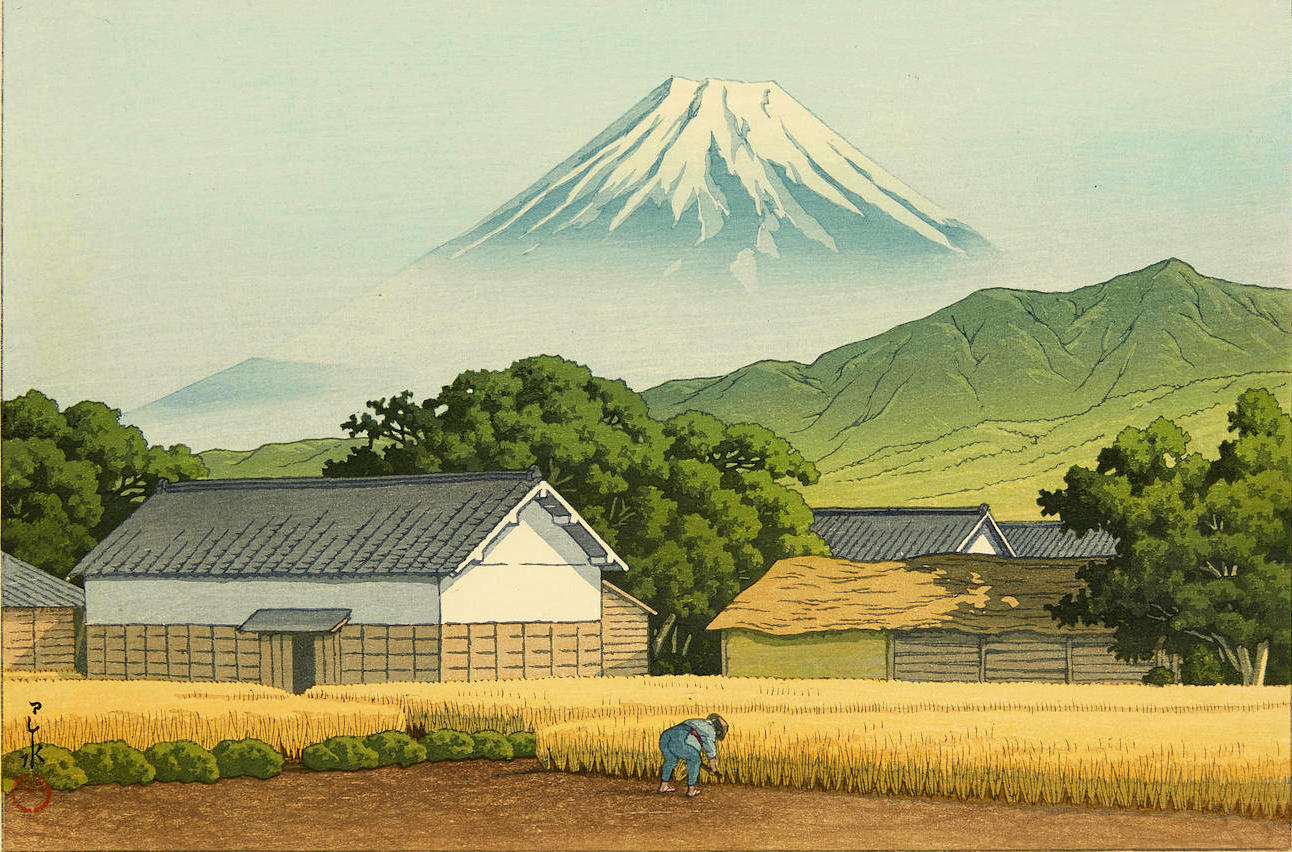

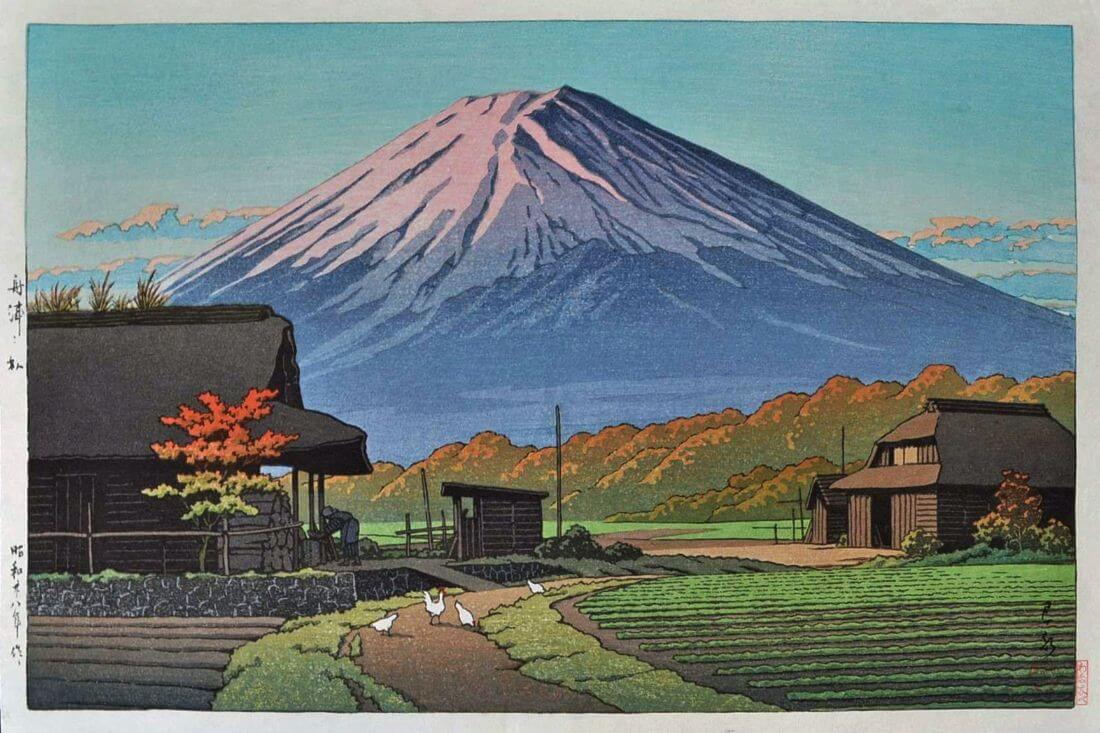
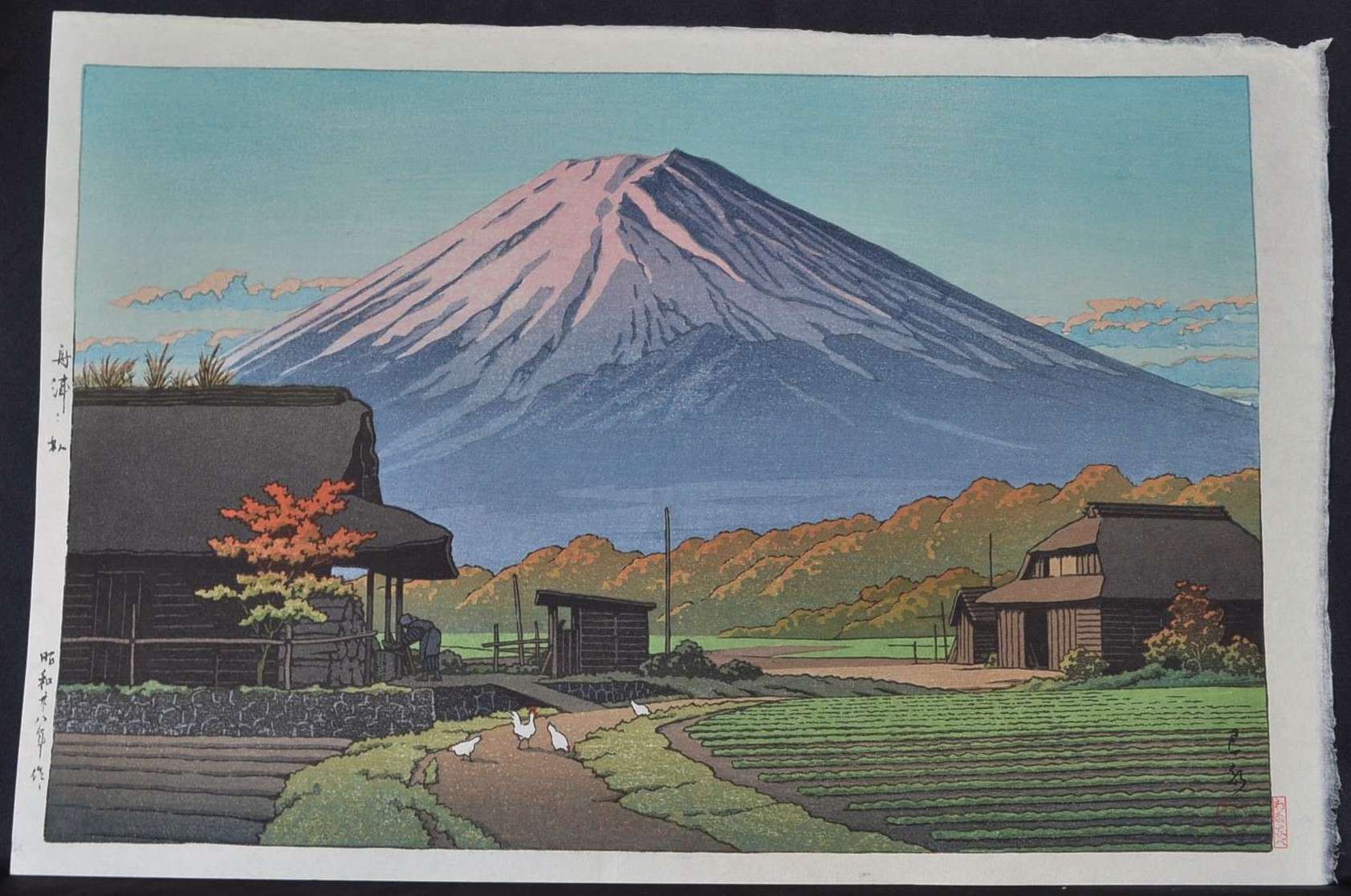
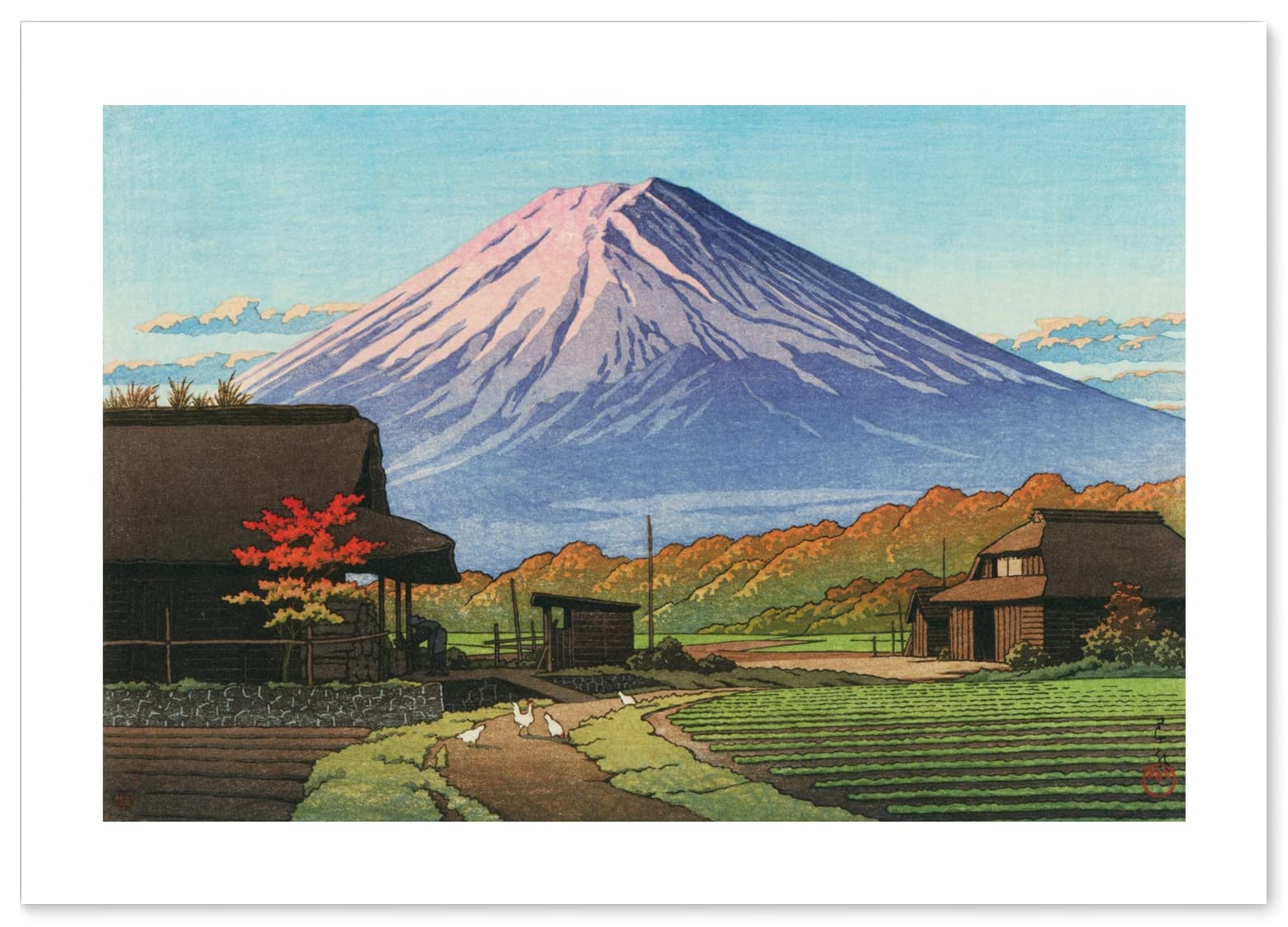
Hasui Kawase – private collection. Title: Mount Fuji from Hara on Tokaido. Date: 1942. Materials: woodblock print. Dimensions: 26.5 x 38.8 cm. Publisher: Watanbe Shozaburo. Sold by Bonhams in New York, on March 20, 2019. Source: https://images2.bonhams.com/image?src=Images/live/2019-02/06/24825871-13-1.jpg. I have changed the light, contrast and colors of the original photo.